* [components][clock_time] Refactor time subsystem around clock_time Introduce the clock_time core with clock source/event separation, high-resolution scheduling, and boot-time helpers, plus clock_timer adapters for timer peripherals. Remove legacy ktime/cputime/hwtimer implementations and migrate arch and BSP time paths to the new subsystem while keeping POSIX time integration functional. Update drivers, Kconfig/SConscript wiring, documentation, and tests; add clock_time overview docs and align naming to clock_boottime/clock_hrtimer/clock_timer. * [components][clock_time] Use BSP-provided clock timer frequency on riscv64 * [risc-v] Use runtime clock timer frequency for tick and delays * [bsp] Add clock timer frequency hooks for riscv64 boards * [bsp] Update Renesas RA driver doc clock_timer link * [bsp] Sync zynqmp-r5-axu4ev rtconfig after config refresh * [bsp][rk3500] Update rk3500 clock configuration * [bsp][hpmicro] Add rt_hw_us_delay hook and update board delays * [bsp][stm32l496-st-nucleo] enable clock_time for hwtimer sample in ci * [bsp][hpmicro] Fix rtconfig include scope for hpm6750evk Move rtconfig.h include outside the ENET_MULTIPLE_PORT guard for hpm6750evk and hpm6750evk2 so configuration macros are available regardless of ENET settings. * [bsp][raspi3] select clock time for systimer * [bsp][hpm5300evk] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][hpm5301evklite] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][hpm5e00evk] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][hpm6200evk] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][hpm6300evk] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][hpm6750evk] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][hpm6750evk2] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][hpm6750evkmini] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][hpm6800evk] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][hpm6e00evk] Trim trailing blank line * [bsp][nxp] switch lpc178x to gcc and remove mcx timer source * [bsp][stm32] fix the CONFIG_RT_USING_CLOCK_TIME issue. * [docs][clock_time] add clock time documentation * [docs][clock_time] Update clock time subsystem documentation - Update device driver index to use correct page reference - Clarify upper layer responsibilities in architecture overview - Update README to describe POSIX/libc, Soft RTC, and device driver usage - Refine architecture diagram with improved layout and color scheme - Remove obsolete clock_timer.md file * [kernel][utest] Trim trailing space * [clock_time] Fix hrtimer wrap handling * [clock_time] fix the static rt_inline issue * [clock_time] fix the rt_clock_hrtimer_control result issue
Titan Board BSP Description
English | Chinese
Introduction
This document provides the BSP (Board Support Package) description for the RT-Thread Titan Board development board. By following the Quick Start Guide, developers can quickly get started with this BSP and run RT-Thread on the development board.
The main contents include:
- Introduction to the development board
- BSP Quick Start Guide
Development Board Introduction
The Titan Board is an RT-Thread development board based on Renesas Cortex-M85 + Cortex-M33 dual-core architecture R7KA8P1 MCU. It provides engineers a flexible and comprehensive development platform, enabling deeper exploration in embedded IoT development.
Titan Board integrates the RA8P1 chip featuring a 1GHz Arm® Cortex®-M85 core and a 250MHz Arm® Cortex®-M33 core. The RA8P1 series is Renesas’ first 32-bit AI-accelerated MCU featuring high-performance Arm® Cortex®-M85 (CM85) with Helium™ vector extensions, and an integrated Ethos™-U55 NPU. It delivers 256 GOPS AI performance, over 7300 CoreMarks, and advanced AI capabilities supporting voice, vision, and real-time analytics.
The front view of the development board is shown below:
Common on-board resources are as follows:
Peripheral Support
The current peripheral support status in this BSP is as follows:
| On-chip Peripheral | Support Status | Component | Support Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| UART | Supported | LWIP | Supported |
| GPIO | Supported | TCP/UDP | Supported |
| CLOCK_TIMER | Supported | MQTT | Supported |
| I2C | Supported | TFTP | Supported |
| WDT | Supported | Telnet | Supported |
| RTC | Supported | Multicore Communication | Support Status |
| ADC | Supported | RPMsg-Lite | Supported |
| DAC | Supported | Extended peripheral | Support Status |
| SPI | Supported | MIPI CSI Camera | Supported |
| RS485 | Supported | CEU Camera | Supported |
| CANFD | Supported | RGB LCD | Supported |
| SDHI | Supported | CYW43438 WIFI | Supported |
| USB | Supported | ||
| HyperRAM | Supported | ||
| HyperFlash | Supported |
Note: The repository provides a minimal system by default. To enable or add additional peripherals, please refer to: Peripheral Driver Usage Guide (rt-thread.org)
User Guide
The user guide is divided into the following two sections:
-
Quick Start
This section is intended for beginners who are just getting started with RT-Thread. By following simple steps, you can run the RT-Thread operating system on this development board and observe the experimental results.
-
Advanced Usage
This section is intended for developers who need to use more board resources on the RT-Thread operating system. By using the FSP and RT-Thread Settings tools to configure the project, more on-board resources can be enabled to achieve advanced functionality.
FSP Version Information
This BSP uses FSP 6.2.0. You must download and install it for peripheral development.
- Download link: rasc-6.2.0
- Note: The BSP provides minimal configuration by default. To enable other peripherals, refer to: Peripheral Driver Usage Guide
Quick Start
This BSP can be directly imported into RT-Thread Studio v2.3.0. The following steps demonstrate how to run the system using RT-Thread Studio.
Install Toolchains
- Install the compiler toolchain:
- Install debugging tools:
Download J-Link v8.48 and PyOCD 0.2.9.
Create a Project
- Click File → Import.
- Select Import RT-Thread BSP, then click Next.
- Select the BSP root directory and fill in project information, then click Finish.
- The project based on the BSP is created.
Configure Debug/Download Settings
Note: Sometimes you may need to modify the settings twice for them to take effect.
Modify the debugger configuration in the Debugger tab.
In the Download tab, change the download method to Flash Hex File, then click OK.
Hardware Connection
Use a USB cable to connect the development board to the PC, and use the DAP-Link interface to download and debug the program.
Build and Download
View Running Results
After the program is successfully downloaded, the system will automatically run and print system information.
Connect the development board’s corresponding serial port to the PC, open the corresponding serial port in a terminal tool (115200-8-1-N), and reset the device. You will then see the RT-Thread output information. Enter the help command to view the commands supported in the system.
\ | /
- RT - Thread Operating System
/ | \ 5.3.0 build Nov 27 2025 13:12:46
2006 - 2024 Copyright by RT-Thread team
==================================================
Hello, Titan Board!
==================================================
msh >help
RT-Thread shell commands:
backtrace - print backtrace of a thread
clear - clear the terminal screen
version - show RT-Thread version information
list - list objects
help - RT-Thread shell help
ps - List threads in the system
free - Show the memory usage in the system
pin - pin [option]
reboot - Reboot System
msh >
Application Entry Function
The entry function of the application layer is located in src\hal_entry.c within void hal_entry(void). User-created source files can be placed directly in the src directory.
#include <rtthread.h>
#include "hal_data.h"
#include <rtdevice.h>
#include <board.h>
#define LED_PIN BSP_IO_PORT_00_PIN_12 /* Onboard LED pins */
void hal_entry(void)
{
rt_kprintf("\n==================================================\n");
rt_kprintf("Hello, Titan Board!\n");
rt_kprintf("==================================================\n");
rt_pin_mode(LED_PIN, PIN_MODE_OUTPUT);
while (1)
{
rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, PIN_HIGH);
rt_thread_mdelay(1000);
rt_pin_write(LED_PIN, PIN_LOW);
rt_thread_mdelay(1000);
}
}
Advanced Usage
Resources and Documentation
- Development Board Official Homepage
- Development Board Datasheet
- Development Board Hardware Manual
- Dualcore Development Guide
- Renesas RA8P1 Group
FSP Configuration
If you need to modify the Renesas BSP peripheral configuration or add new peripheral interfaces, you will need to use the Renesas Flexible Software Package (FSP) configuration tool. Please make sure to follow the steps below for configuration. If you encounter any issues, you may ask questions in the RT-Thread Community Forum.
- Download Flexible Software Package (FSP) | Renesas, please use FSP version 6.2.0
- Refer to the documentation: Configuring Peripheral Drivers Using FSP for the RA Series.
- Configure development by importing FSP:
Users can locate the configuration.xml file in the project and import it into FSP to start configuration:
Select File → Open at the top-left corner to open the configuration file.
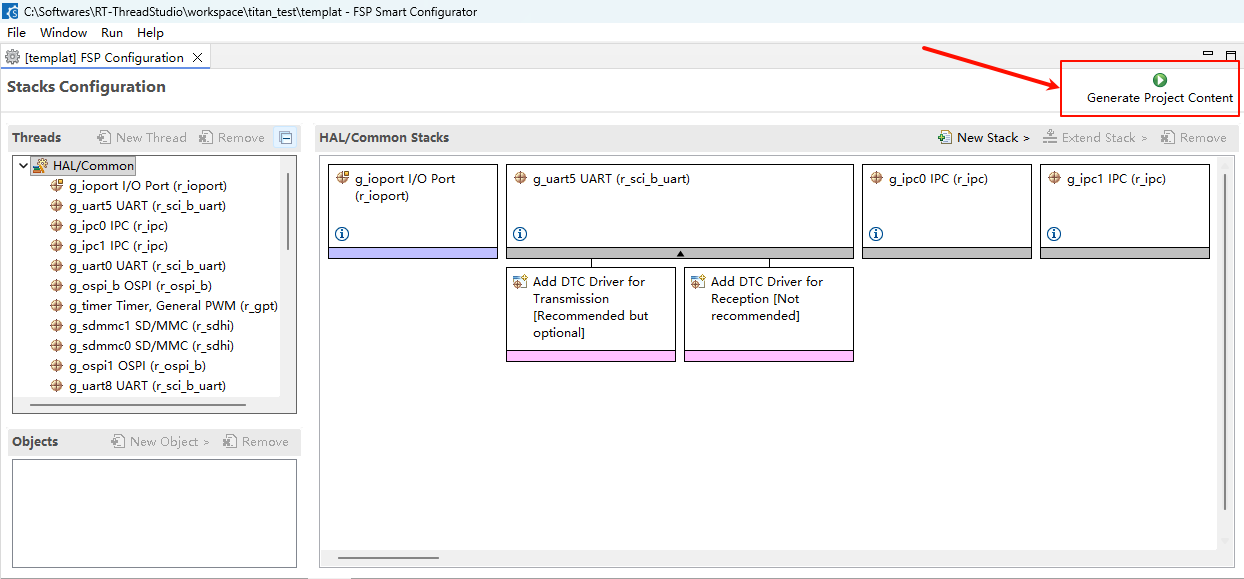
- Generate FSP Code:
RT-Thread Settings
In RT-Thread Settings, you can configure the RT-Thread kernel, components, software packages, and Titan Board device drivers.
Contact Information
If you have any thoughts or suggestions during usage, please feel free to contact us via the RT-Thread Community Forum.
Contribute Code
If you're interested in Titan Board and have some exciting projects you'd like to share, we welcome code contributions. Please refer to How to Contribute to RT-Thread Code.